Google has released an extensive whitepaper that delves into the development, architecture, and applications of Generative AI agents. This detailed document sheds light on how these advanced AI systems operate, emphasizing their ability to use external tools to expand their functionality far beyond the limits of traditional language models.
Defining Generative AI Agents
The whitepaper defines a Generative AI agent as an advanced application designed to achieve specific objectives by observing its environment, making decisions, and acting upon it using external tools. These agents are distinguished by their autonomy, enabling them to function independently of human intervention when given clear goals and guidelines.
“Agents extend the capabilities of language models by leveraging tools to access real-time information, suggest real-world actions, and plan and execute complex tasks autonomously,” the authors explain. This autonomy allows agents to navigate complex problem spaces, making them highly effective in scenarios requiring dynamic decision-making and execution.
Core Architecture and Cognitive Framework
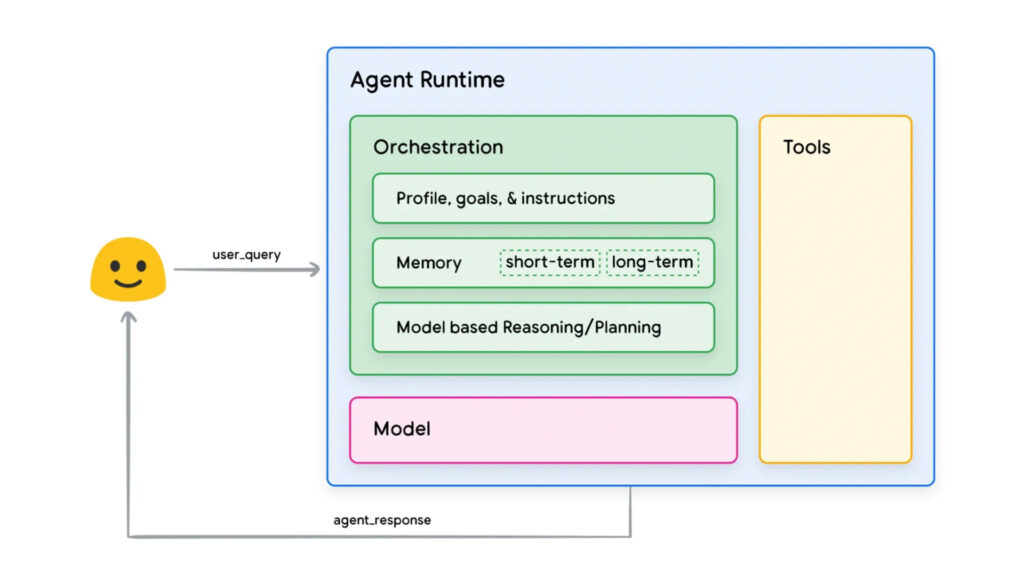
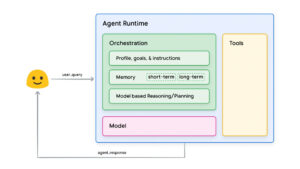
The whitepaper outlines the architecture of these agents, highlighting several key components that enable their sophisticated functionality:
- Cognitive Framework: This component structures the agent's reasoning, planning, and decision-making processes. It provides the foundational logic necessary for interpreting inputs, analyzing options, and formulating strategies to achieve desired outcomes.
- Orchestration Layer: Acting as a control hub, the orchestration layer guides agents through a cyclical process of information intake and action execution. It ensures that the agent can continuously refine its understanding of the environment and adapt its strategies in real time.
- External Tools and Functions: Tools such as Extensions and APIs allow agents to interact with external systems. These tools empower agents to perform tasks like updating databases, retrieving real-time information, or interfacing with specialized software, greatly enhancing their versatility.
“Tools bridge the gap between the agent’s internal capabilities and the external world,” the authors note. For example, by using APIs, an agent can fetch the latest stock prices, analyze them, and provide actionable insights.
Dynamic Data Access with Data Stores
The integration of Data Stores plays a crucial role in ensuring agents maintain access to dynamic, up-to-date information. By leveraging Data Stores, agents can ensure their outputs remain relevant, accurate, and aligned with the latest available data. This capability is particularly significant in scenarios such as financial analysis or logistics, where changing conditions require instant adaptability.
Practical Applications of Generative AI Agents
The whitepaper explores a range of practical applications where Generative AI agents can add value. For example:
- Travel Booking Assistance: An agent could assist users in booking flights by interacting with multiple APIs to gather real-time information on flight schedules, pricing, and availability. It can then compare options and present the best recommendations tailored to the user’s preferences.
- Customer Support: AI agents could autonomously handle customer queries, troubleshoot issues, or provide product recommendations, reducing the workload on human teams while improving response times.
- Enterprise Integration: Within organizations, agents can be deployed to manage workflows, update internal databases, or generate reports, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
Developer Tools and Integration Platforms
Google also emphasizes how developers can harness the power of Generative AI agents using platforms like Vertex AI. Vertex AI provides a managed environment for creating and deploying AI agents, enabling developers to define goals, craft task instructions, and provide training examples. This simplifies the process of building tailored AI solutions that align with specific organizational needs.
Broader Industry Implications
The whitepaper’s release comes as the broader tech industry increasingly explores the potential of AI agents in transforming workflows and boosting productivity. OpenAI’s CEO, Sam Altman, echoed this sentiment in his recent blog post titled Reflections, predicting that AI agents could join the workforce as early as 2025.
“We believe that, in 2025, we may see the first AI agents join the workforce and materially change the output of companies,” Altman wrote. His vision aligns with the growing consensus that AI agents will play a pivotal role in reshaping industries ranging from healthcare and finance to logistics and customer service.
Conclusion
Google’s whitepaper offers a comprehensive roadmap for understanding the evolving landscape of Generative AI agents. By detailing their architecture, capabilities, and practical applications, the document serves as a valuable resource for developers, researchers, and businesses looking to harness the power of these autonomous systems. As AI agents become increasingly sophisticated, their potential to revolutionize industries and redefine human-AI collaboration continues to grow.





































































































Validate your login
Sign In
Create New Account